Introduction
Picture this: You’re preparing for a drone mission to capture critical aerial data. Maybe it’s for ecological research, inspecting infrastructure, or surveying land for development. The area includes open fields, wetlands, and a nearby communication tower that serves as a key waypoint for your operation.
As you check the weather, you notice the visibility is reported at 1.5 miles, and the cloud ceiling sits at 600 feet. These conditions immediately raise red flags. The FAA requires at least 3 statute miles of visibility to ensure you can safely maintain visual line-of-sight with your drone and identify other aircraft in the area.
Exam Prep
On the Part 107 exam, you’ll encounter images of sectional charts and be asked to identify all kinds of information
Defining Cloud Ceilings
Aviation defines Cloud Ceiling as:
- the height above ground of the lowest cloud cover that is broken or overcast,
- or the vertical visibility into fog or other obstructions.

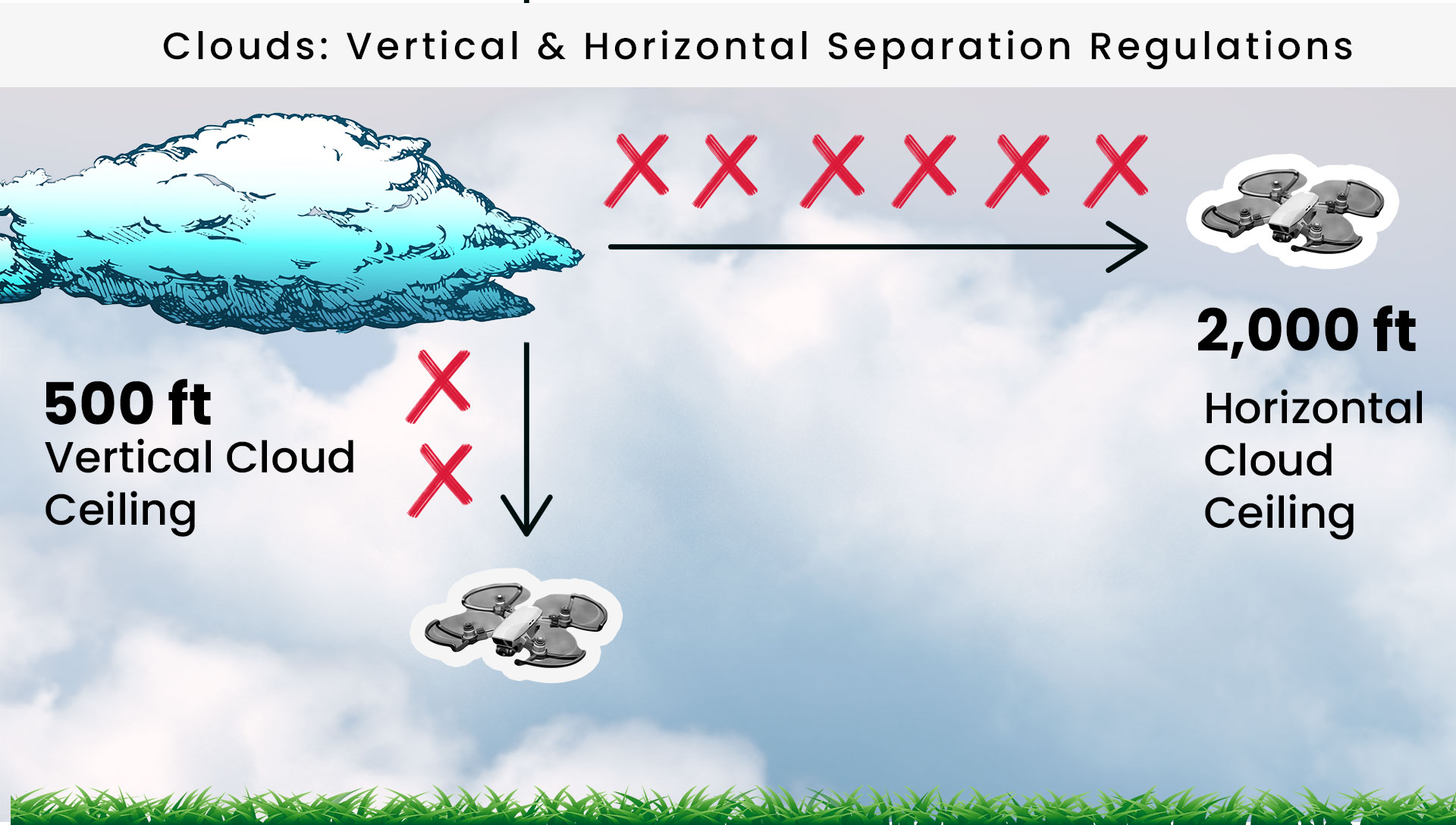
What are the FAA’s Vertical and Horizontal Cloud Ceilings?
500 Foot Vertical Cloud Ceiling
- Flight must be kept at least 500 feet below a cloud ceiling, keeping safe separation between the UA and the lowest layer of clouds.
2000 Foot Horizontal Cloud Ceiling
- The sUAS must be kept at least 2,000 feet horizontally from a cloud. This horizontal distance reduces the likelihood of the drone entering into clouds.
When sUAS Tower Inspections and Cloud Ceilings Combine

Tower Inspection Regulations
Remember, sUAS are only allowed to operate higher than 400 feet AGL when inspecting a structure, but they must remain within a 400-foot radius of the structure.
For example, if you are inspecting a tower that is 1,000 feet tall, you can legally fly up to 1,400 feet AGL, provided you stay within a 400-foot radius of the tower.
- 1,000 feet for the structure height + 400 feet for the allowable altitude above the structure
Inspecting a Tower with a Cloud Ceiling:
When inspecting a tower, the FAA’s standard 400-foot AGL maximum altitude regulation changes. In this scenario, you’re allowed to fly up to the top of the tower, plus an additional 400 feet above and within a 400-foot radius of its structure.
However, this doesn’t mean you can ignore maintaining a minimum 500-foot vertical distance from cloud layers.
To inspect the top of a 1,104-foot tower while remaining compliant with FAA regulations, you must maintain a minimum vertical distance of 500 feet below any cloud layer. This means the cloud ceiling must be at least 500 feet higher than the top of the tower.
Adding the tower’s height (1,104 feet AGL) to the required 500-foot separation gives a total of 1,604 feet AGL.
Therefore, the lowest possible cloud ceiling that allows you to inspect the very top of the tower is 1,604 feet AGL.

Sectional Chart Practice
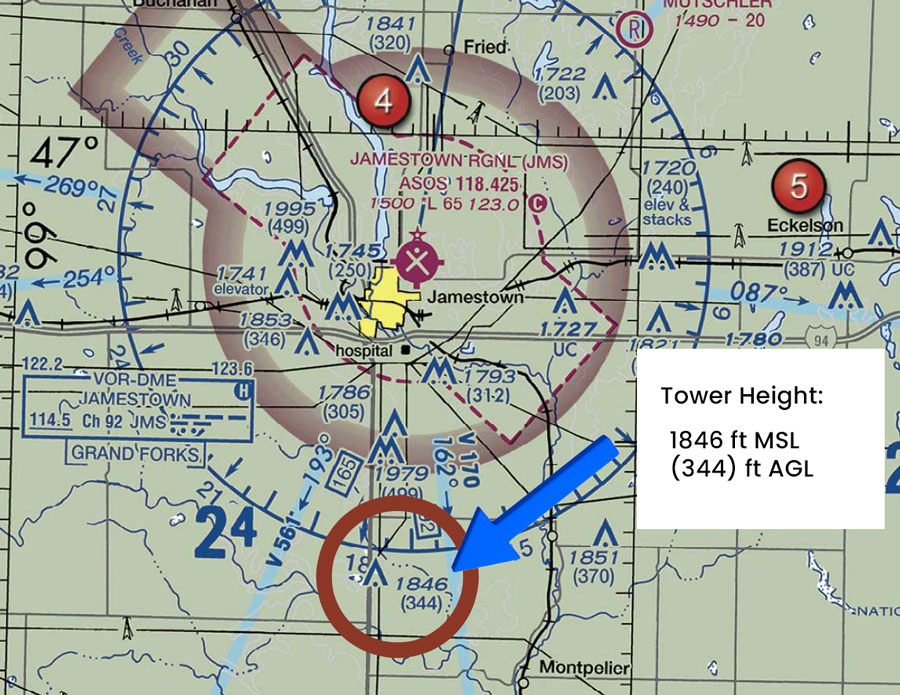
Example: Tower Outside of Jamestown Regional Airport
You are inspecting the lighted towers approximately 10 NM South of the Jamestown Regional Airport (JMS). What is the lowest cloud cover that will enable you to inspect the top of the tower.
Correct Answer:
2,346 ft MSL or
844 feet AGL
Explanation:
On sectional charts, tower heights are listed with the top number in Mean Sea Level (MSL) and the bottom number in Above Ground Level (AGL). The MSL number shows the tower’s height from sea level, while the AGL number tells you how tall it is from the ground.
In this case, upon finding the tower 10NM South of Jamestown Airport, we see that its MSL is shown to be 1,846 feet, and its AGL is shown to be (344) ft.
We know that the minimum distance the sUAS can fly below clouds must be no less than 500 feet.
Therefore the minimum cloud ceiling to legally inspect the very top of the towers becomes:
1,846 + 500 = 2,346 feet MSL
344 + 500 = 844 AGL feet AGL