Before every flight, solid flight planning starts with a good look at sectional charts. You’ll need to scout out key details to keep your operation safe and smooth. This might mean spotting caution boxes for glider activity, noting max altitudes in areas like mountain ranges, or avoiding surprises like tethered weather balloons.
Let’s break down the must-know elements to check before you head out.
Landmarks and Notifications
Check Notification Boxes:
Prepare for Any Important Information Specific to The Area
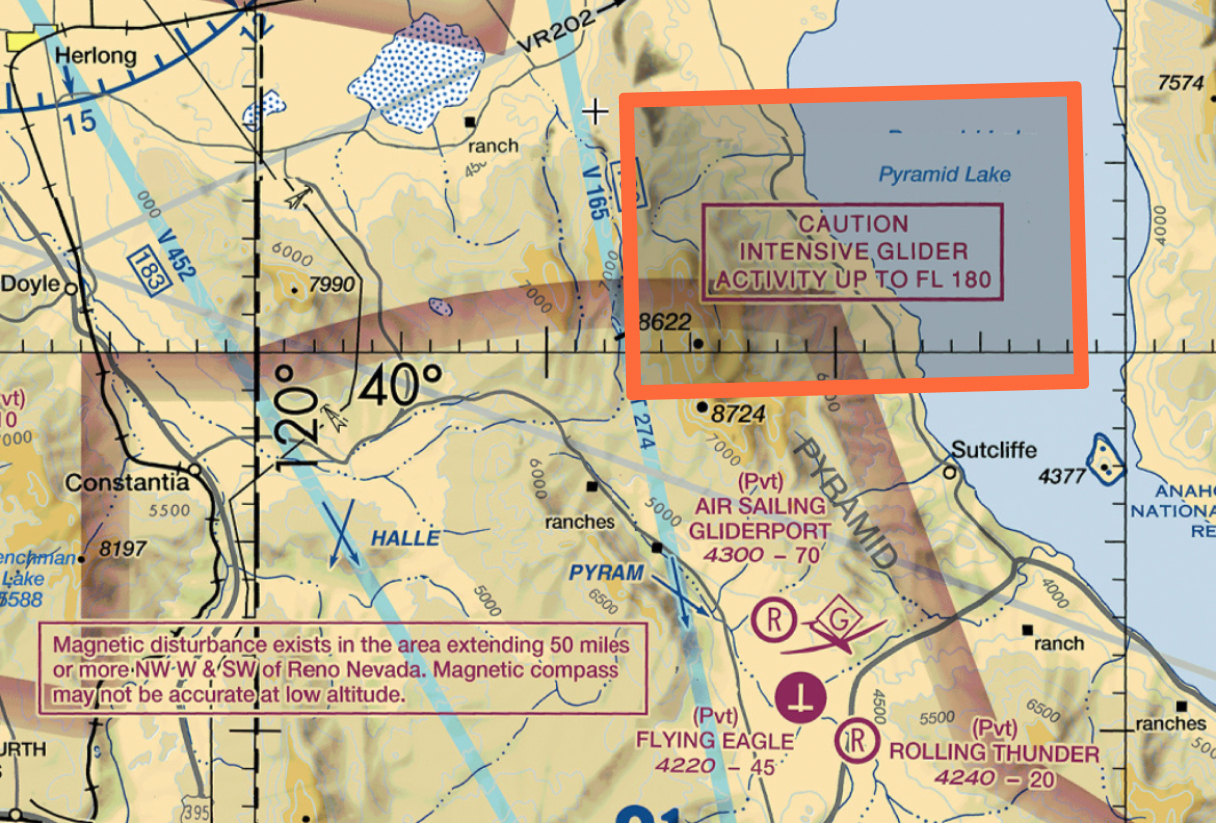
These provide highly important details that could impact your flight, like temporary flight restrictions (TFRs) or special activities (parachuting, aerial events). Remember, accidents can happen, including a fly away rogue drone you wouldn’t want going anywhere near a glider.
Notice in the example below there are 2 notification boxes. One explains intensive glider activity up to 180 feet AGL, something you absolutely would want to avoid as a drone pilot.
The other is more of a geographical fact that you’d want to know: That within a 50 mile radius of Reno Nevada there is an anomaly of a magnetic disturbance, and your compass may not be accurate at low altitude. This is something you’d likely only if you checked the sectional chart for the area.
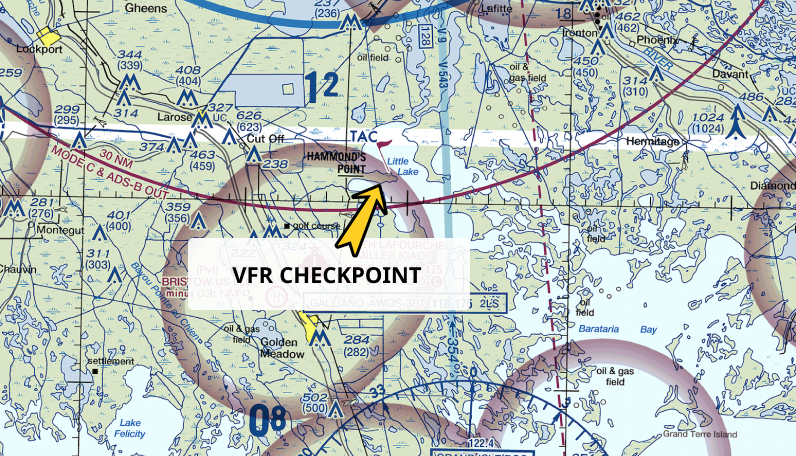
Check VFR Checkpoints:
Expect High Levels of Manned Aircraft
A VFR (Visual Flight Rules) checkpoint is a designated location on the ground that helps pilots navigate from the sky, often near busy airspace like airports or congested flight paths. These checkpoints are marked by a magenta flag on a sectional chart, and they’re typically used by manned aircraft to ensure they stay on course during visual flight.
Now, as a drone pilot, you might wonder why you’d care about a VFR checkpoint, especially since they’re meant for manned aircraft. Well, the key is that these checkpoints are often located in high-traffic areas, where planes are flying visually, meaning you’ll likely encounter more aircraft.
Knowing where these checkpoints are can help you steer clear of busy flight paths and avoid any potential run-ins with manned aircraft. It’s smart to be aware of where these checkpoints are located—especially if you’re flying near airports or in controlled airspace. It keeps your flight safe and helps you plan accordingly.
Geographic Features

Isogonic Lines
Check Isogonic Lines:
Make Sure Your Compass is Calibrated
Isogonic lines are lines drawn on maps that show areas of equal magnetic declination. Magnetic declination is the difference between the direction of magnetic north (which your compass points to) and true north (the geographic North Pole). Since the Earth’s magnetic field isn’t uniform everywhere, the declination changes depending on where you are. Isogonic lines show you areas where the magnetic declination is the same, helping pilots and navigators understand how much their compass will differ from true north.
Now, here’s where it gets interesting: the scientist who discovered these lines was Halley, as in Edmond Halley—yes, the same guy who gave his name to Halley’s Comet. Back in the late 1600s, Halley was one of the first to notice that magnetic declination was different depending on where you were on Earth. He studied this and plotted the lines of equal declination, eventually making them part of navigational maps to help people with compass readings.
Why are these lines on maps today? Well, back in the days of sailors and early aviators, knowing the magnetic declination was critical for navigating accurately, especially when using compasses. By marking isogonic lines on maps, navigators could easily adjust their course to account for the magnetic deviation in different regions. Today, it’s still useful for pilots, drone operators, and anyone using magnetic navigation tools.
MEFs
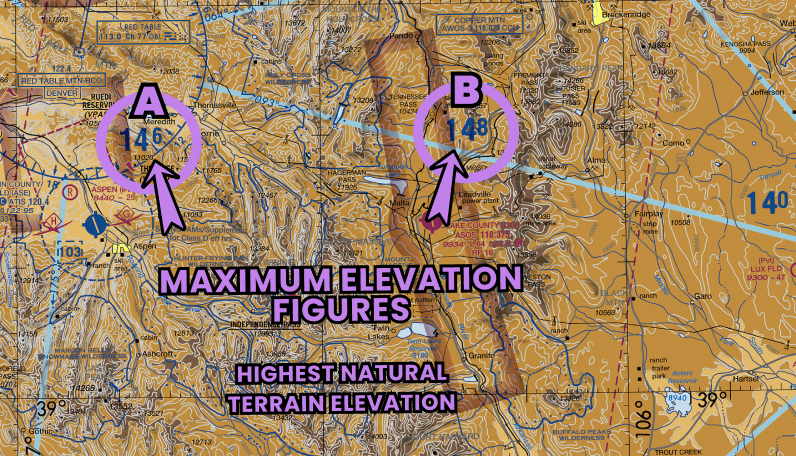
Check Maximum Elevation Figures
Prepare for Terrain, Max Elevation, and Obstacles Ahead
Maximum Elevation Figures (MEFs) on a sectional chart are the highest elevations of terrain and obstacles (like towers or buildings) within a specific area, rounded up to the next hundred feet. They are shown in feet above sea level and are marked in areas between contour lines. These figures give pilots and drone operators a heads-up about the highest point they could potentially fly over in that area.
For drone pilots, MEFs matter because they help you avoid crashing into tall objects or terrain. If you’re flying in an area with a mountain range, for instance, knowing the MEF will tell you the highest point to be aware of. This is especially important for drone operators since, unlike manned aircraft, drones don’t usually have the same altitude clearance, and even a slight error in altitude could result in a collision with an obstacle.
And remember, from Section 1 of this course, if you crash your drone, you must report it to the FAA within 10 days! 😉
Aerial Activities

Gliders & Parachutes
Check for Parachute Jumping Areas
Parachute and Glider Zones: Know Before You Fly
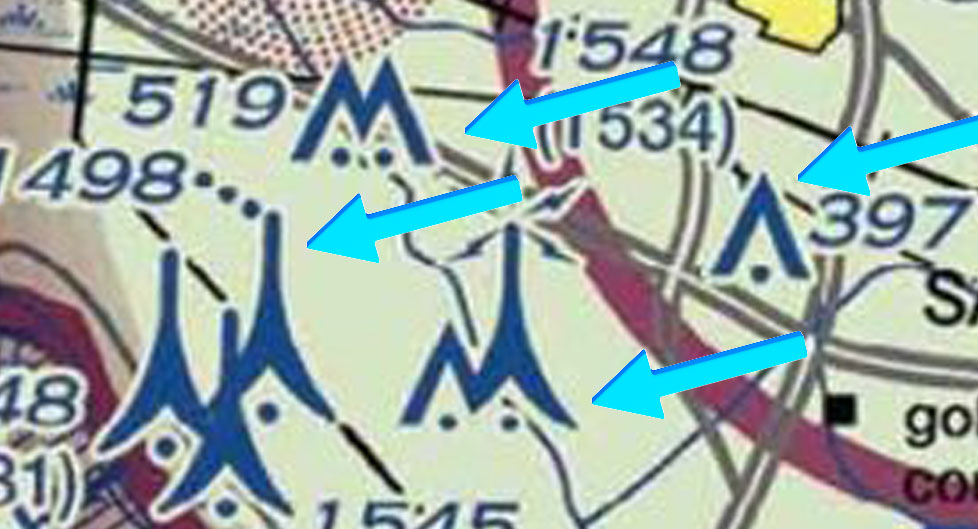
Parachute jumping and glider operations are marked on sectional charts with easy-to-spot symbols.
- Parachute Jumping Areas: Shown with a parachute symbol, these areas may include notes like drop zone names or general altitude ranges.
- Glider Operations: Represented by a glider symbol, indicating areas with regular soaring activity or glider ports.
However, the sectional chart provides only basic info. For more details, including times and schedules, pilots should check the Chart Supplement, which includes:
- Exact locations, altitudes, and times for parachute zones.
- Communication frequencies for coordinating with airfield staff.
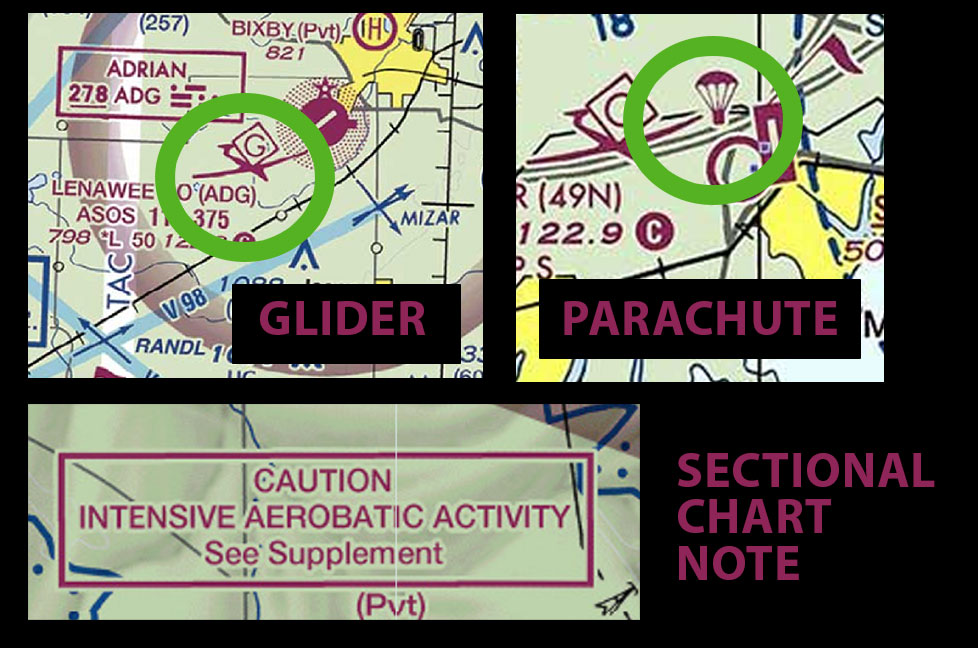
Above: Use Sectional Chart to spot locations
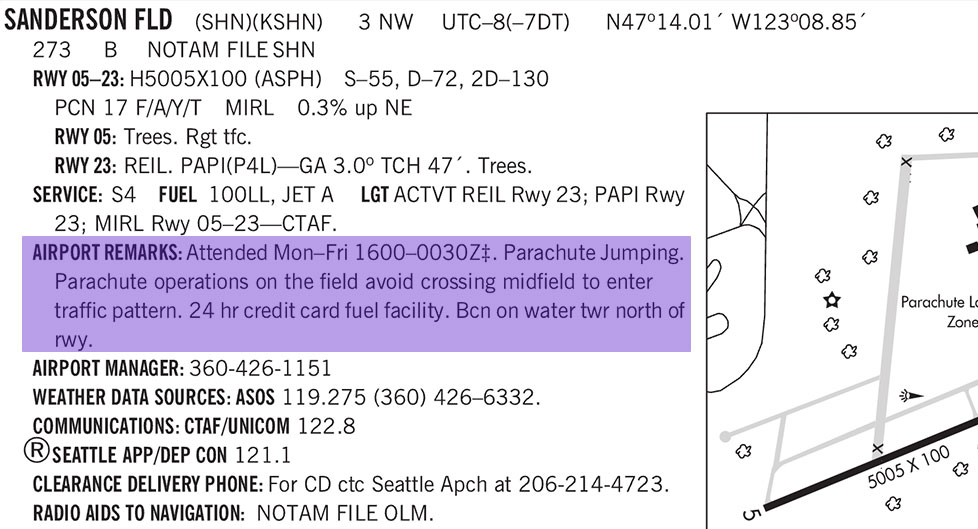
Above: Use Chart Supplement for Detailed Parachute / Glider Info
Structures & Obstructions

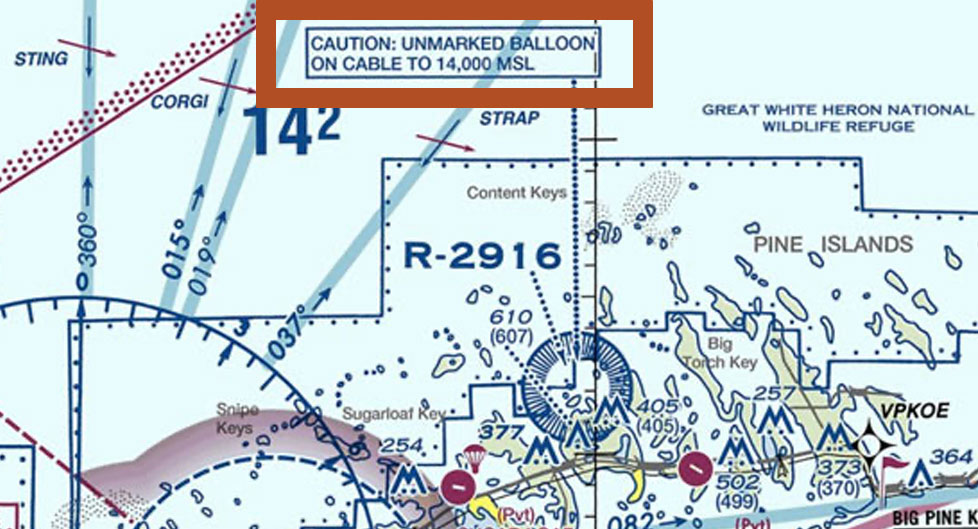
Weather Balloons
Check for Unmarked Weather Balloons:
Avoid Unseen Hazards
Represent tethered weather balloons. The sectional chart legend provides their altitudes, and you must remain aware of their locations to avoid tether interference.

Towers
Towers: Individual, Grouped, and Lighted
Know Their Location and Height
Marked with symbols indicating heights (AGL and MSL) and lighting status for visibility. Grouped structures list the tallest point.
We’ll go over these in another section in a more detailed manner.