Introduction to Altitude Measurements
AGL: Above Ground Level
A height measured with respect to the underlying ground surface.
When an aircraft is flying at a certain AGL altitude, it refers to the distance between the aircraft and the ground or any elevated object, like a building.
AGL provides a reference point for pilots to help navigate safe altitudes above obstacles like buildings, mountains, wildfires, and towers.
MSL: Mean Sea Level
A standard measurement of a location’s vertical distance relative to a historical average sea level.
In aviation, MSL provides a consistent reference point, not affected by the variations of the Earth’s terrain.
| Abbreviation | Stands For | Zero Level |
|---|---|---|
| AGL | Above Ground Level | Zero |
| MSL | Mean Sea Level | Sea Level Average |
In general,”altitude” refers to distance above mean sea level (MSL), “height” refers to distance above a particular point (e.i. the airport or ground at present location), and “elevation” describes a feature of the terrain itself in terms of distance above MSL.
Confusion between AGL and MSL, or improper calibration of the altimeter, may result in controlled flight into terrain, or a crash of a fully functioning aircraft under pilot control.
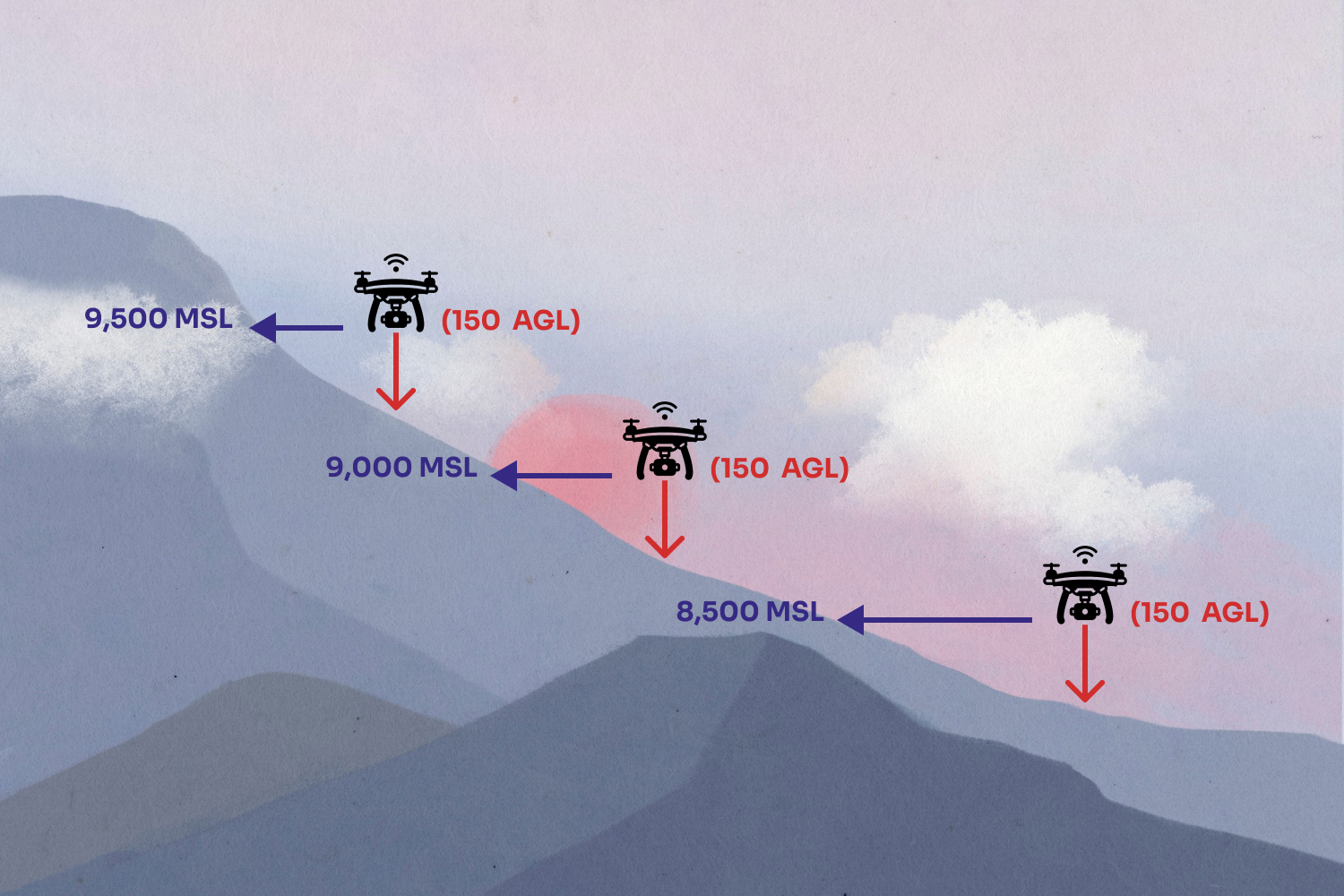
3 Examples of AGL & MSL in the Field
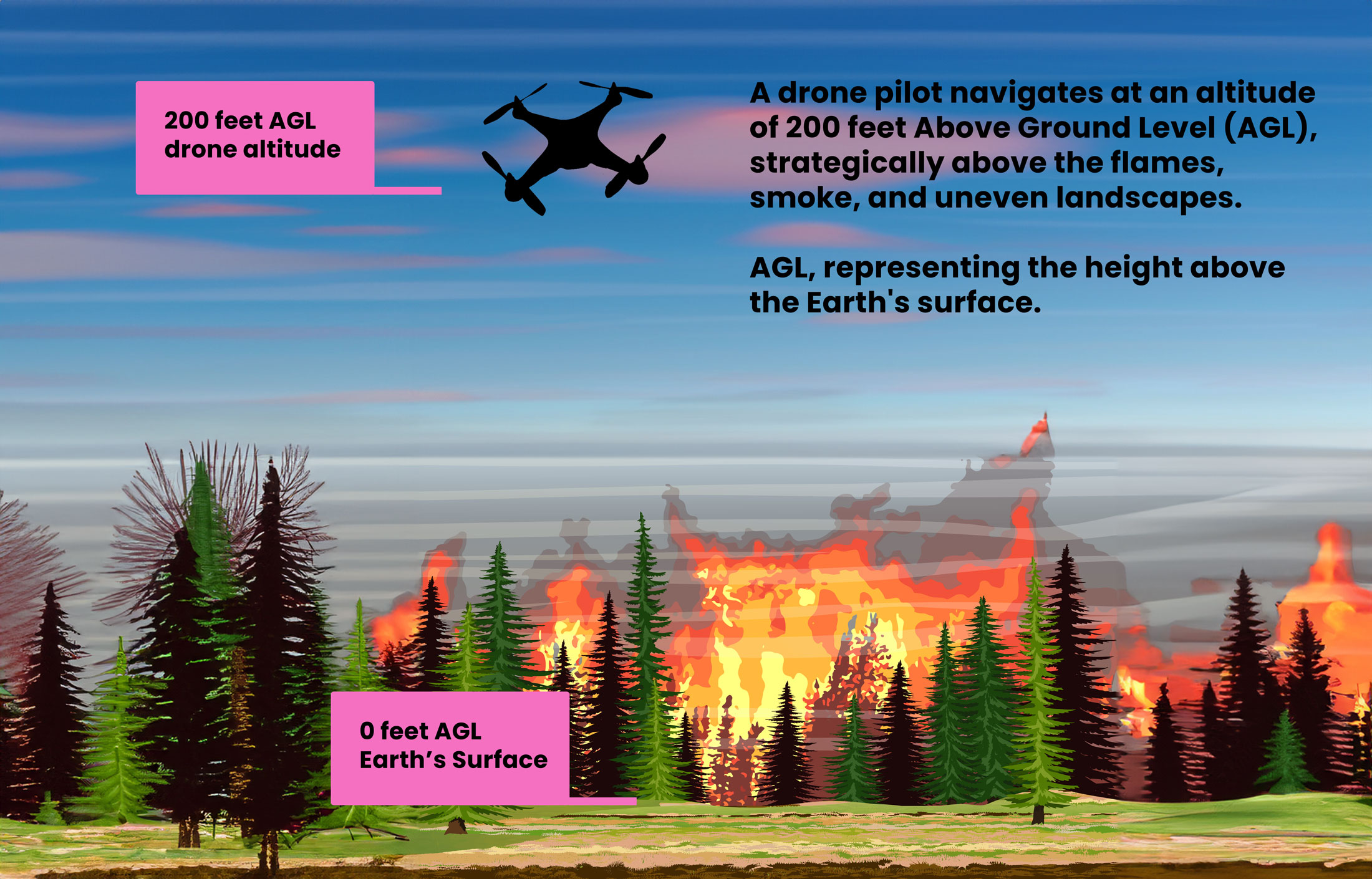
1. AGL Altitude in Flight: Wildfire Operations in California
California has dry, windy, and often hot weather conditions from spring through late autumn that can produce moderate to severe wildfires.
Equipped with thermal imaging and real-time mapping capabilities, drones offer immediate insights into fire behavior, spread, and intensity, enabling quicker and more informed decision-making. This technology also enhances situational awareness for firefighters, allowing for more efficient resource allocation and better protection of at-risk areas.
In this case, if you and your team are working with firefighters during a fire where the flames and trees are averaging a maximum height of 100 feet AGL, you should strategically keep the sUAS above the flames, smoke, and uneven landscape, flying it at, for example, 200 feet AGL.
Knowing AGL (Above Ground Level) is key here because it keeps the drone safe above obstacles and gives firefighters the clear data they need.
2. MSL Altitude in Flight: Coastal Surveys
Drones play an important role in studying Mean Sea Level (MSL) by providing high-resolution mapping of coastlines and capturing precise elevation data. They collect real-time information on tidal and storm surges, which aids in flood mapping and disaster response. They also monitor the impact of rising sea levels on coastal ecosystems and detect saltwater intrusion in agricultural areas.
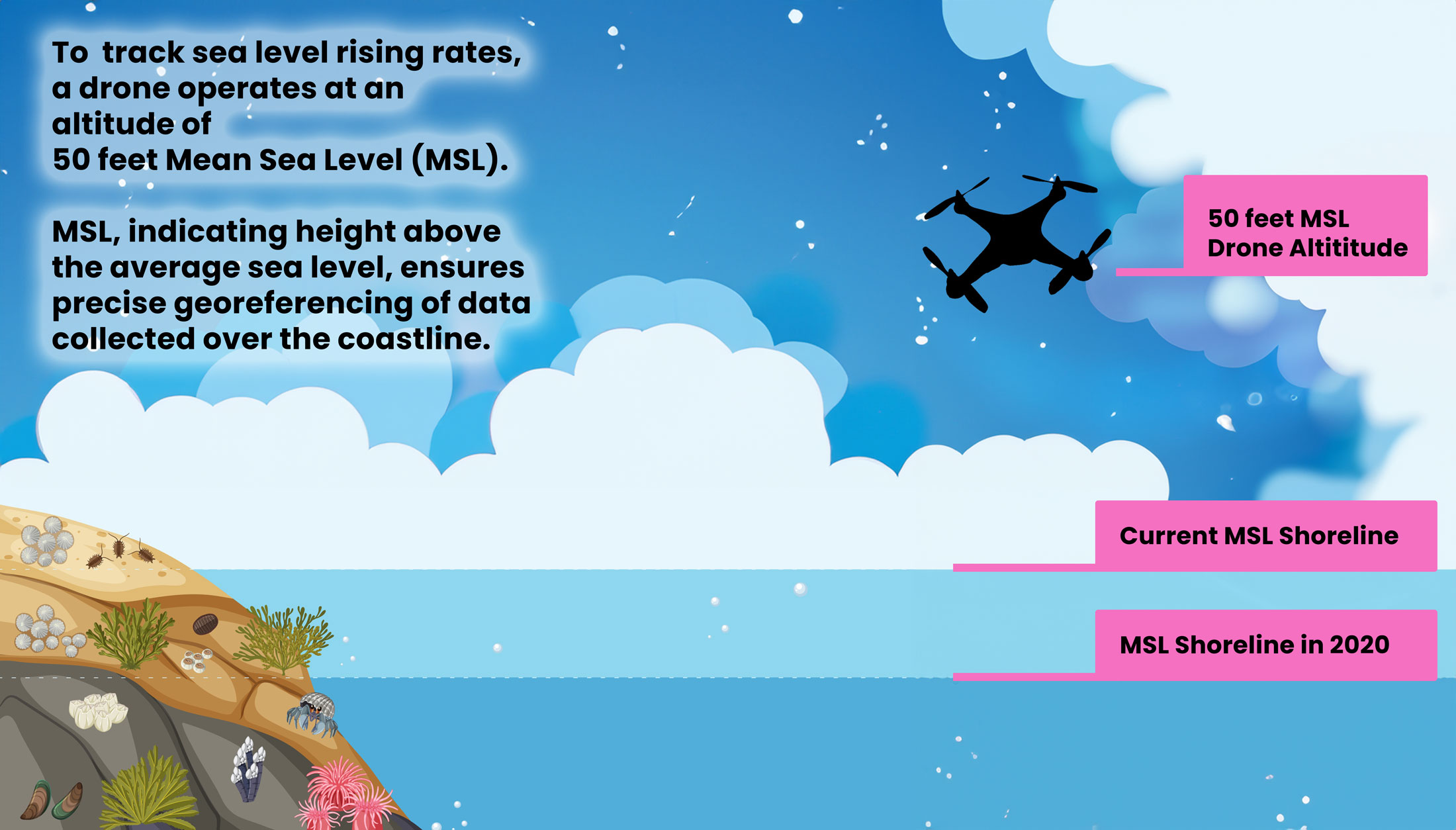
Let’s say an sUAS is involved in a in coastal survey along the Gulf of Mexico to monitor rising sea levels. The sAUS operates at an altitude of 50 feet Mean Sea Level (MSL).
This standardized reference allows precise georeferencing of data collected along the coastline to facilitate accurate monitoring of coastal changes and the impacts of sea level rise.
By maintaining a consistent altitude above MSL, the drone effectively tracks variations in coastal features, providing valuable insights for scientific research and coastal management strategies.
3. MSL & AGL In Flight: Search and Rescue in the Rocky Mountains
Drones play an important role in studying Mean Sea Level (MSL) by providing high-resolution mapping of coastlines and capturing precise elevation data. They collect real-time information on tidal and storm surges, which aids in flood mapping and disaster response. They also monitor the impact of rising sea levels on coastal ecosystems and detect saltwater intrusion in agricultural areas.
Let’s say an sUAS is involved in a in coastal survey along the Gulf of Mexico to monitor rising sea levels. The sAUS operates at an altitude of 50 feet Mean Sea Level (MSL).
This standardized reference allows precise georeferencing of data collected along the coastline to facilitate accurate monitoring of coastal changes and the impacts of sea level rise.
By maintaining a consistent altitude above MSL, the drone effectively tracks variations in coastal features, providing valuable insights for scientific research and coastal management strategies.

3 Examples of AGL & MSL in the Field
Practice Question:
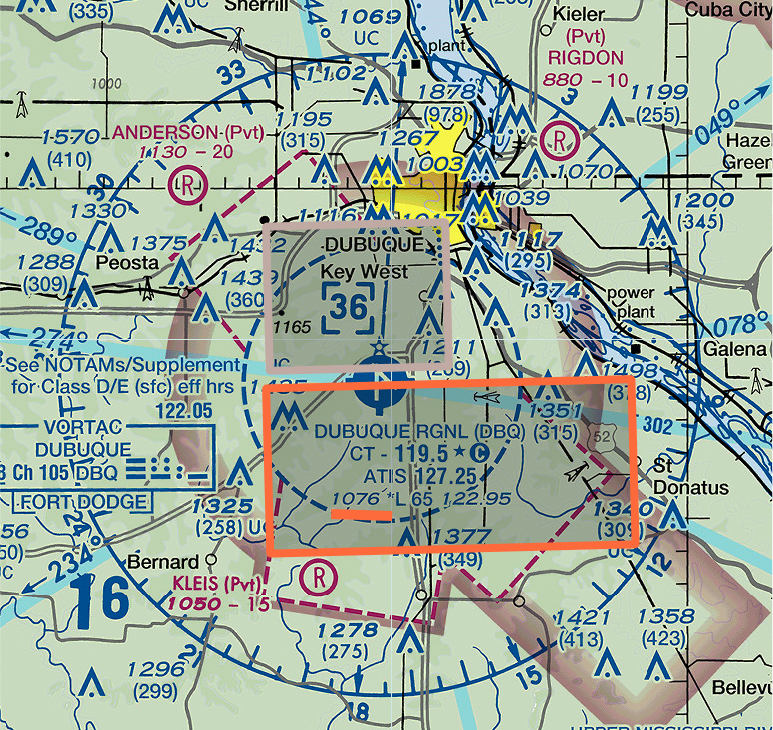
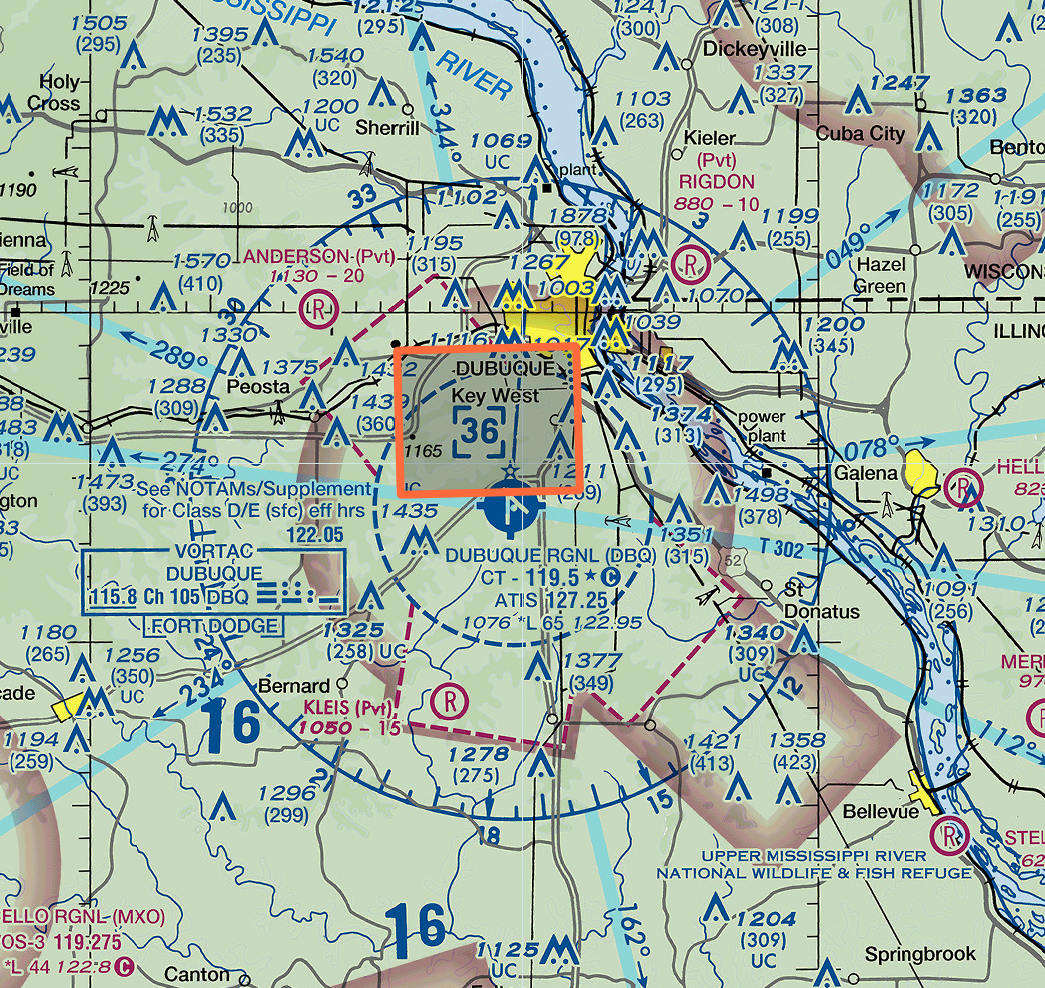
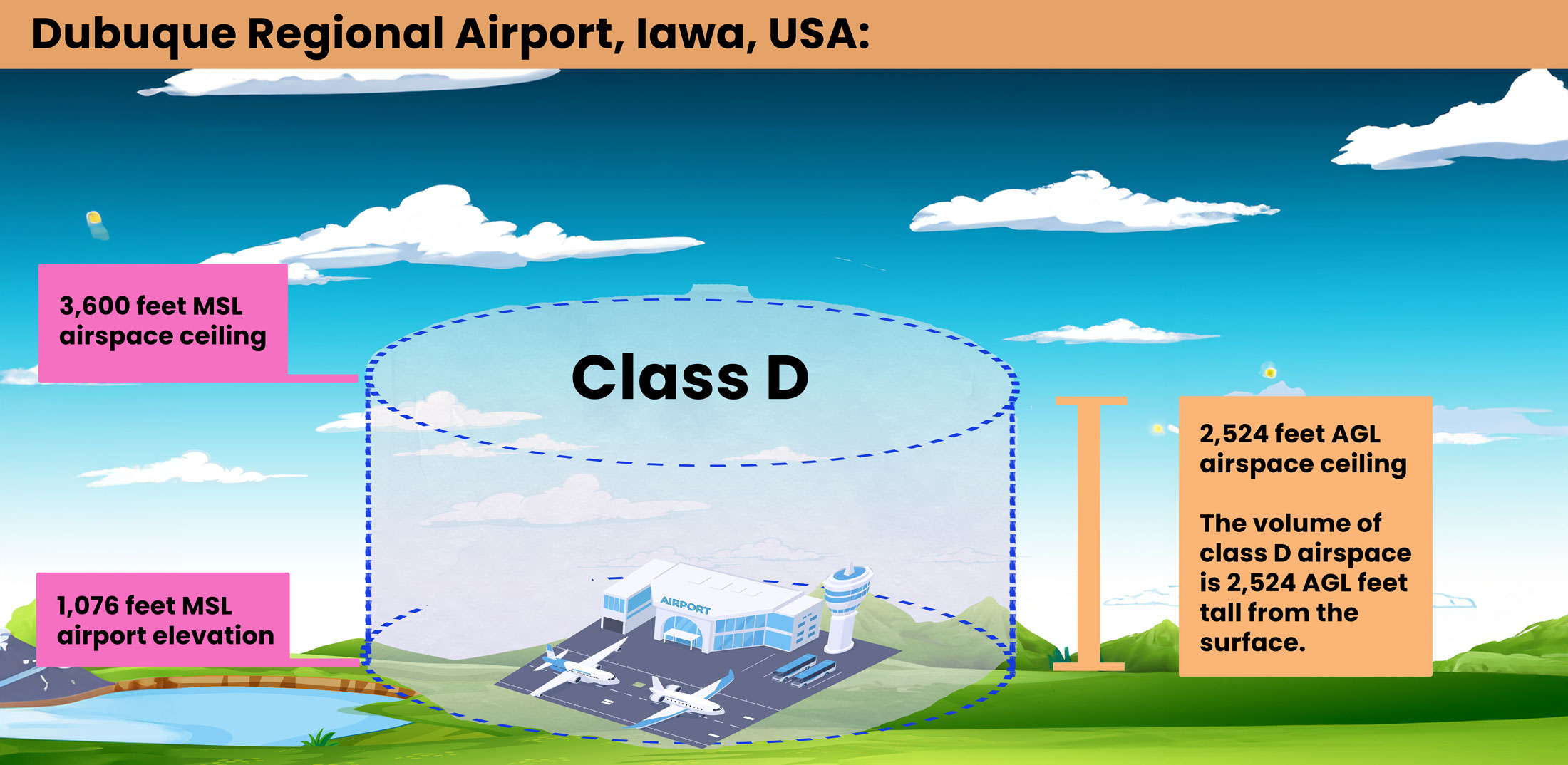
What is the top altitude of the Dubuque Regional Airport Class D Airspace in AGL?
Dubuque Regional Airport (DBQ) is located in Dubuque, Iowa, United States. It is a Class D airspace.
We want to determine how high above the ground level the top of the Class D airspace extends.
Knowing the top altitude of the airspace in AGL helps pilots, especially drone operators, know at what altitude they need to fly to avoid entering controlled airspace.
Let’s walk through the simple subtraction equation we need to find that information out:
First, note the key height and elevation figures of DBQ Airport.
- Airport Height: Figure 1 shows the airport sits at 1,076 MSL, according to the airport legend.
- Airspace Hight: Figure 2 shows the top of Class D airspace reaches 3,600 MSL, marked in the blue-cornered box.
Second, let’s do a little subtraction math (use the visual aid below for a diagram of what we’re working with)
To find the altitude in AGL, you subtract the airport’s elevation (1,076 feet MSL) from the MSL altitude of the airspace ceiling (3,600 feet).
This calculation (3,600 feet MSL – 1,076 feet MSL) results in 2,524 feet AGL.
Therefore, we know that in terms of height from the surface, that DBQ airport is 2,524 feet tall. So, a drone pilot would need to fly at least 2,524 feet AGL to remain clear of the Class D airspace.
Quick Review
Height of Airspace in AGL?
Airport Elevation is at 2,100 feet MSL and Airspace Ceiling is at 4,600 feet MLS.Calculation:
4,600 feet MSL – 2,100 feet MSL = 2,500 feet AGL.
Therefore, we know this airspace extends 2,500 feet above the ground level.
Height of Airspace in AGL?
Airport elevation is at 1,500 feet MSL and airspace ceiling is at 3,800 feet MSL.Calculation:
3,800 feet MSL – 1,500 feet MSL = 2,300 feet AGL.
Therefore, we know this airspace extends 2,300 feet above the ground level.
Height of Airspace in AGL?
Airport elevation is 800 feet MSL and the top of Class C airspace is at 3,200 feet MSL.Calculation:
3,200 feet MSL – 800 feet MSL = 2,400 feet AGL.
This means the top of Class C airspace is located 2,400 feet above the ground level.
Practice Quiz