
Introduction
Thunderstorms with lighting in sight are amazing to watch! However, they are absolutely not what you want to encounter while on an sUAS flight mission. Here’s the story on thunderstorms to help you know what to look out for in the field.
Exam Prep
On the Part 107 exam, you’ll encounter images of sectional charts and be asked to identify all kinds of information
3 Phases of a Thunderstorms Life Cycle
The whole process takes about one hour for an ordinary thunderstorm. Severe thunderstorms like supercells and squall lines are much larger, more powerful, and last for several hours.
Phase 1: Cumulus Phase:
- Marks the beginning of a thunderstorm’s life cycle
- Vigorous Updrafts
- Developing Cumulus Clouds
Thunderstorms begin within a type of cloud called a cumulonimbus, which is a towering, vertically developed cloud often associated with intense weather.
During this stage, masses of moisture are lifted upwards into the atmosphere. As warm, moist air is lifted upwards, it begins to cool, condense, and form cumulus clouds. These clouds grow rapidly, powered by updrafts, which are the strong currents of rising air that carry the moisture higher into the atmosphere.
This first phase of thunderstorms features vigorous updrafts and the sedeveloping cumulus clouds, signifying the initial phase of a thunderstorm’s life cycle.
As the cloud matures and more moisture accumulates, the cloud’s internal dynamics intensify, leading to the second phase.
Definition to Note: Cumulonimbus Clouds are towering, vertically-developed clouds with a distinctive anvil-shaped top.
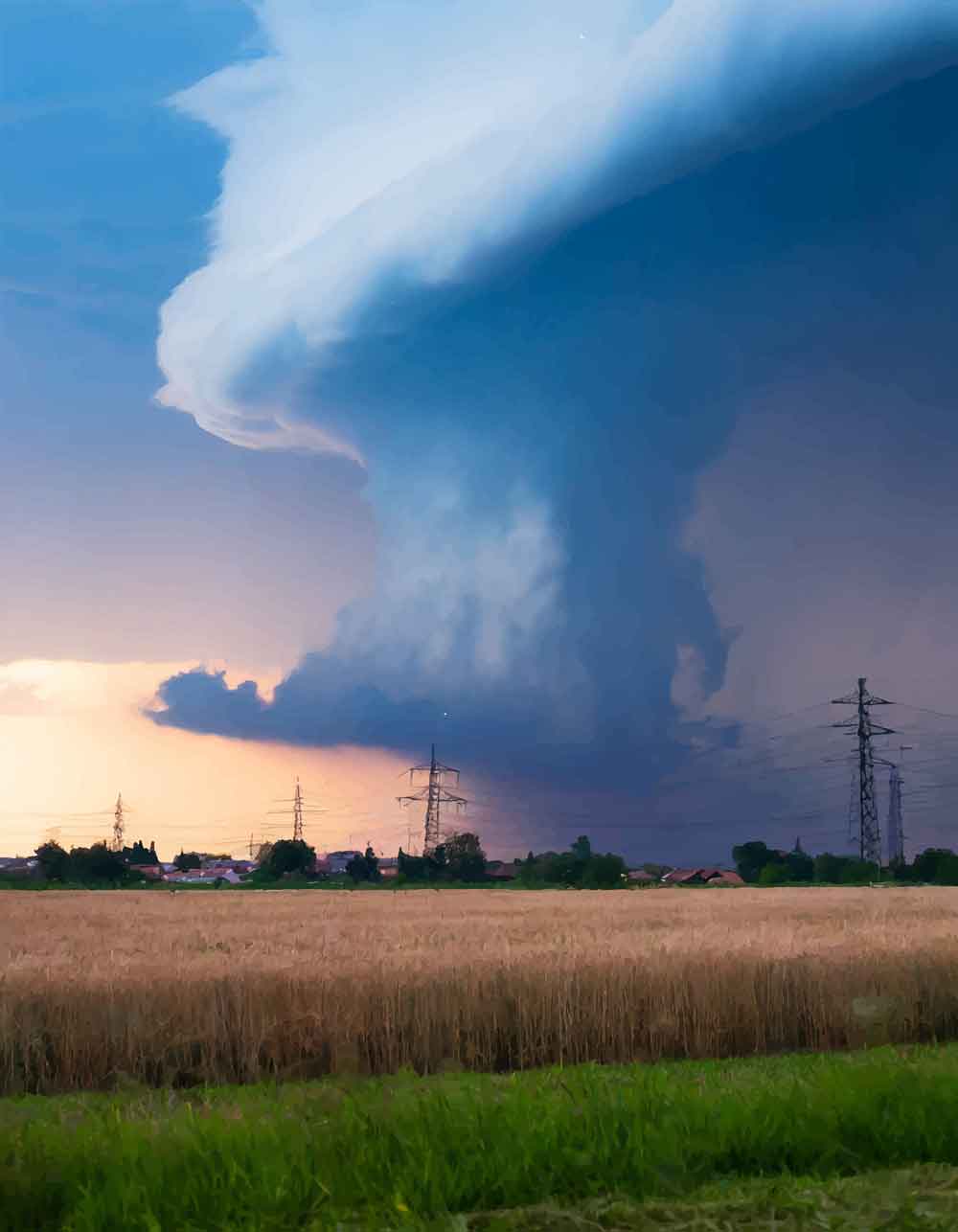

Phase 2: Mature Stage
- Greatest intensity of the storm
- Updrafts and Downdrafts
- Precipitation begins
- Cumulonimbus cloud has fully developed
- Anvil shape forms at top of cloud
The mature stage of a thunderstorm is when it reaches its most intense and active phase. During this stage, the cumulonimbus cloud fully develops and extends high into the atmosphere, forming the characteristic anvil shape. The anvil cloud is the upper part of the storm that spreads out horizontally once the updrafts hit the stratosphere, creating a flat, wide top that can resemble the shape of an anvil.
In this phase, the updrafts continue to push moisture upward, while downdrafts develop as cooler, heavier air sinks. This interaction between rising and sinking air creates turbulence and fuels the storm’s energy, leading to intense weather like lightning, thunder, and heavy precipitation (rain or hail).
Downdrafts occur when water droplets in the cloud grow heavy enough to fall to the ground, contributing to the distinguishing feature of the start of precipitation during the mature stage of the storm.
As the storm peaks, severe weather such as hailstorms, tornadoes, and flash flooding can occur. The mature stage typically lasts 15 to 30 minutes before the storm begins to weaken, signaling the transition to the dissipation stage.

Phase 3: Dissipating Stage
- Storm weakens
- Downdrafts Increase
- Updrafts Stop
In the dissipating stage, the storm begins to lose strength as the downdrafts dominate, and the storm’s upward air currents weaken. The overall storm’s intensity starts to decrease. The dissipating stage is when the storm begins to lose its structure and energy, and the cloud gradually breaks apart.
The storm dies out with light rain as the cloud disappears from bottom to top.
3 Conditions Needed for Thunderstorms
In order for thunderstorms to happen, the following 3 elements must be present.
Moisture

There needs to enough water vapor moisture in the air. (This is why thunderstorms frequently occur when the humidity level is high.)
This water vapor provides the building blocks needed to create clouds and precipitation in the form of rain or storms.
Unstable air conditions

Unstable conditions mean that as you go higher in the sky, the air gets colder quickly.
This rapid cooling lets warm air near the ground rise easily, which starts the process of making big thunderstorm clouds called cumulonimbus clouds.
A lifting force (upward boost)
Thunderstorms result from the rapid upward movement of warm, moist air.
It requires:
Something to Lift the Air: There needs to be a force, like a front (meeting of air masses), a mountain, or the rising lift of hot air rising from the ground.
Trigger for Upward Motion: This force acts as a trigger, lifting the warm, moist air, starting the process that leads to the development of thunderstorms.
Hazards Related to Thunderstorms
Windshear
Lighting
(Consistently associated with thunderstorms)
Consistently associated with thunderstorms because it results from the buildup and discharge of electrical energy within the storm clouds.
Lightning is the most hazardous circumstance when operating an sUAS in close proximity to thunderstorms because any lightning strike within the vicinity can potentially damage or destroy the drone’s electronics.
Hail
Thunderstorms can also bring hail, small balls of ice, which can hit areas far from the storm, including where you’re flying your drone. Don’t assume you’re safe just because the storm seems far away—hail, even small pieces, can damage your drone.
Turbulence
Thunderstorms are notorious for generating severe turbulence, especially in their mature stage. The intense updrafts and downdrafts within this stage can create sudden and strong changes in air movement making sUAS control difficult.
Icing
Thunderstorms at high altitudes create supercooled water droplets that freeze on aircraft surfaces. Icing on drones increases weight, disrupts aerodynamics, reduces lift, and can lead to loss of control.
Microbursts
Thunderstorms can create microbursts, which are sudden, strong winds that blow downward. Microbursts can cause aircraft to drop quickly and are very dangerous during takeoff or landing.
Wind Shear
Wind shear refers to a sudden change in wind speed or direction over a short distance, either horizontally or vertically, within the atmosphere. It can occur at any altitude and is especially important during weather events like thunderstorms, where it can have a significant impact on aircraft performance and safety.
Squall Lines
(Most dangerous kind of thunderstorm to aircarft)
Squall line thunderstorms are the most dangerous to aircraft because they produce severe weather such as high winds, hail, turbulence, and tornadoes. These storms are often associated with cold fronts and wind shear, which contribute to their rapid intensification and potential for widespread damage, flash flooding, and dangerous flying conditions.
Tornadoes
Tornadoes can potentially develop from any cloud linked to a severe thunderstorm, even if it’s many miles from the main thunderstorm cloud.
Key Items to Remember
- Lighting is consistently associated with thunderstorms and is the most hazardous circumstance when operating an sUAS in close proximity to thunderstorms given your sAUS can get struck by lightning midair.
- Wind Shear is a sudden change in wind direction and speed.
- A squall line is a long, narrow line of intense thunderstorms that can bring strong winds, heavy rain, hail, and sometimes tornadoes. It is the most hazardous type of storm.
SIGMETS: Vital Weather Warnings
SIGMETs deliver vital weather advisories during flights, offering essential information that enhances flight safety. They are among the best resources for understanding and preparing for adverse weather conditions along your route.
- Surface winds gusting at 45 knots or above.
- Hail measuring 1 inch in diameter or larger.
- Tornado occurrences.
- Embedded, line, or area thunderstorms.
- Severe thunderstorms rated at VIP level 5 or higher that affect 50% or more of an area of at least 4,000 square miles.
Quick Review
Flash Cards
Vigorous Updrafts
are part of which thunderstorm stage?Cumulus Stage
Stage 1Peak Intensity
are part of which thunderstorm stage?Mature Stage
Stage 2Anvil-shaped Cloud
are part of which thunderstorm stage?Dissipating Stage
Stage 3
Powerful Updrafts & Downdrafts
are part of which thunderstorm stage?Mature Stage
Stage 2 (accompanied by precipitation)
Cumulonimbus Clouds
are part of which thunderstorm stage?Cumulus Stage
Stage 1
Downdrafts Increase & Updrafts Cease
are part of which thunderstorm stage?Dissipating Stage
Stage 3
Rain Starts
are part of which thunderstorm stage?Mature Stage
Stage 2 (start of rain signals start of mature stage)
Weakening Storm
are part of which thunderstorm stage?Dissipating Stage
Stage 3 (marking the concluding phase of the thunderstorm’s life cycle)




