Introducing the
3 Axes of Motion:
Roll, Yaw, and Pitch
The axes of motion refer to the three fundamental directional movements (pitch, roll, and yaw) that control the orientation and movement an sUAS.
Roll
Roll is the side-to-side tilt of an sUAS, which allows it to bank left or right.
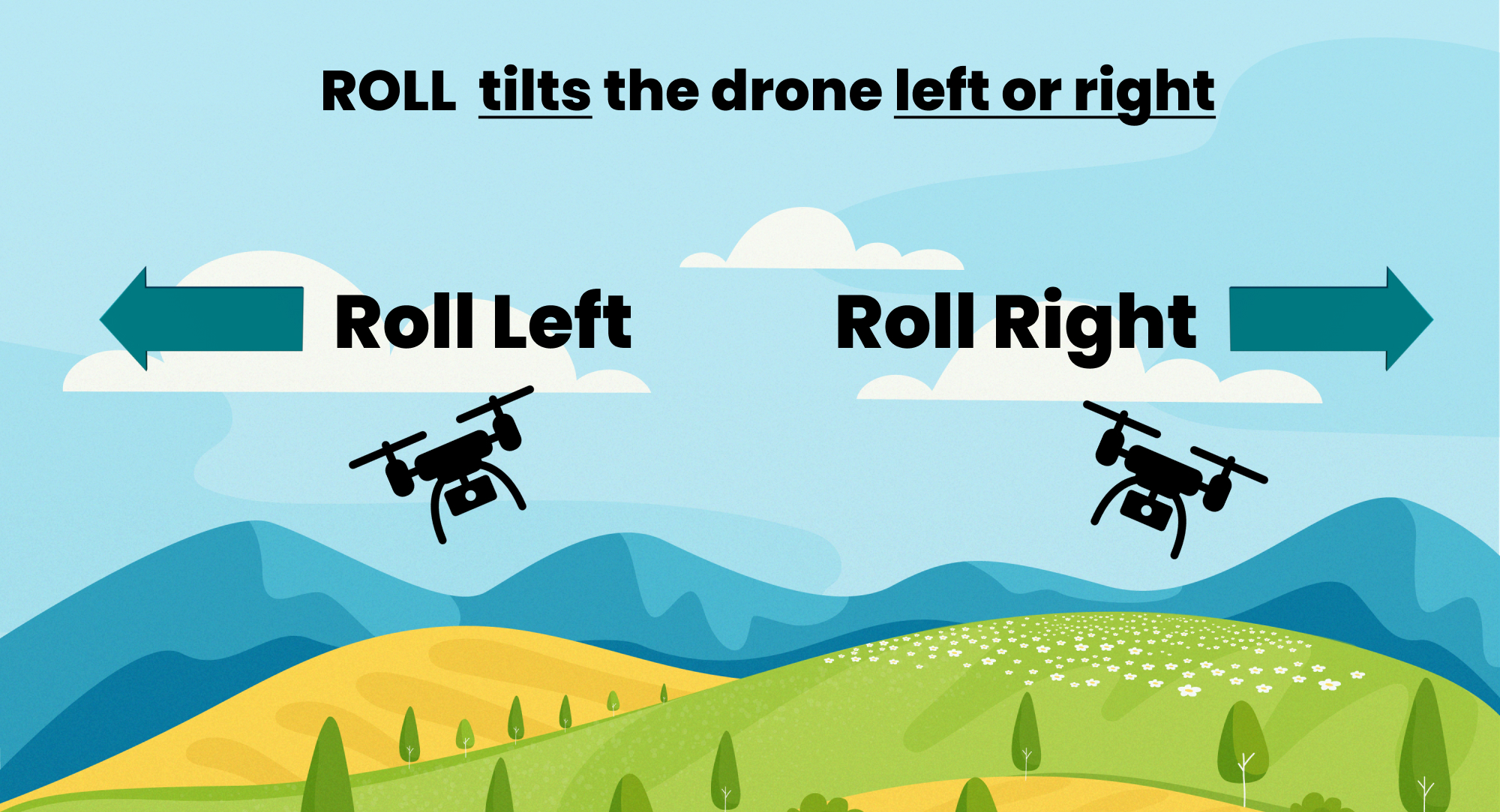
How It Roll Works
- Component Involved:
- The roll control is handled by the drone’s ailerons.
- Function:
- A drone’s ailerons are used to control roll, which is the rotation of the sUAS around its front-to-back axis. By tilting one aileron up and the other down, the sUAS can tilt its body to one side or the other, allowing it to bank in the desired direction.
- Example:
- If the left aileron is pushed down and the right aileron is lifted, the sUAS will roll to the left.
- If the right aileron is pushed down and the left aileron is lifted, the sUAS will roll to the right.
Yaw
Yaw is the movement of the drone around its vertical axis, making the drone turn left or right without changing its tilt.
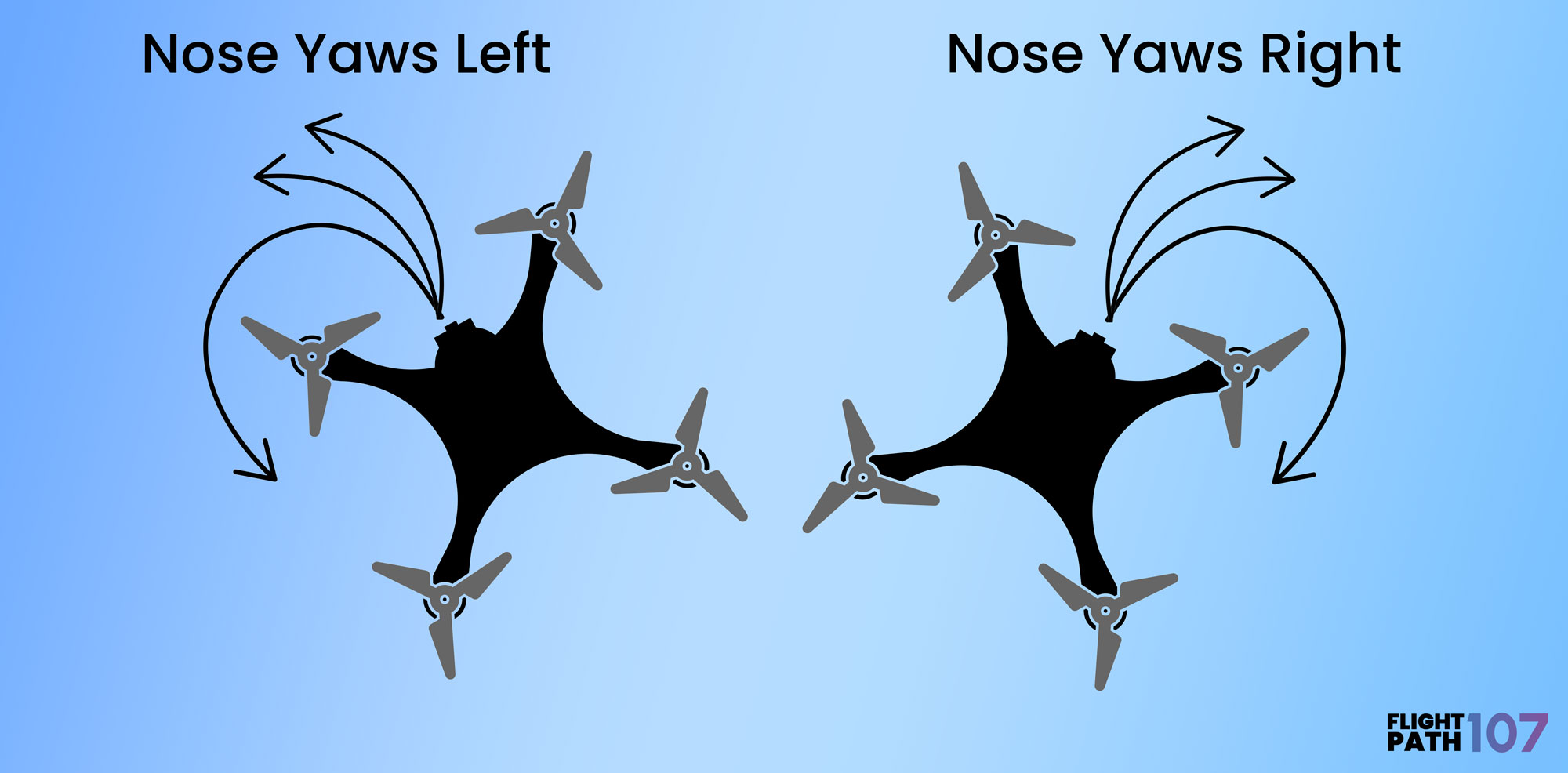
How It Roll Works
The difference in motor speeds ultimately allows for a perfectly balanced spin along its central axes, allowing the drone to be turned left or right.
Pitch
Pitch affects how the drone climbs, descends, or maintains its altitude.
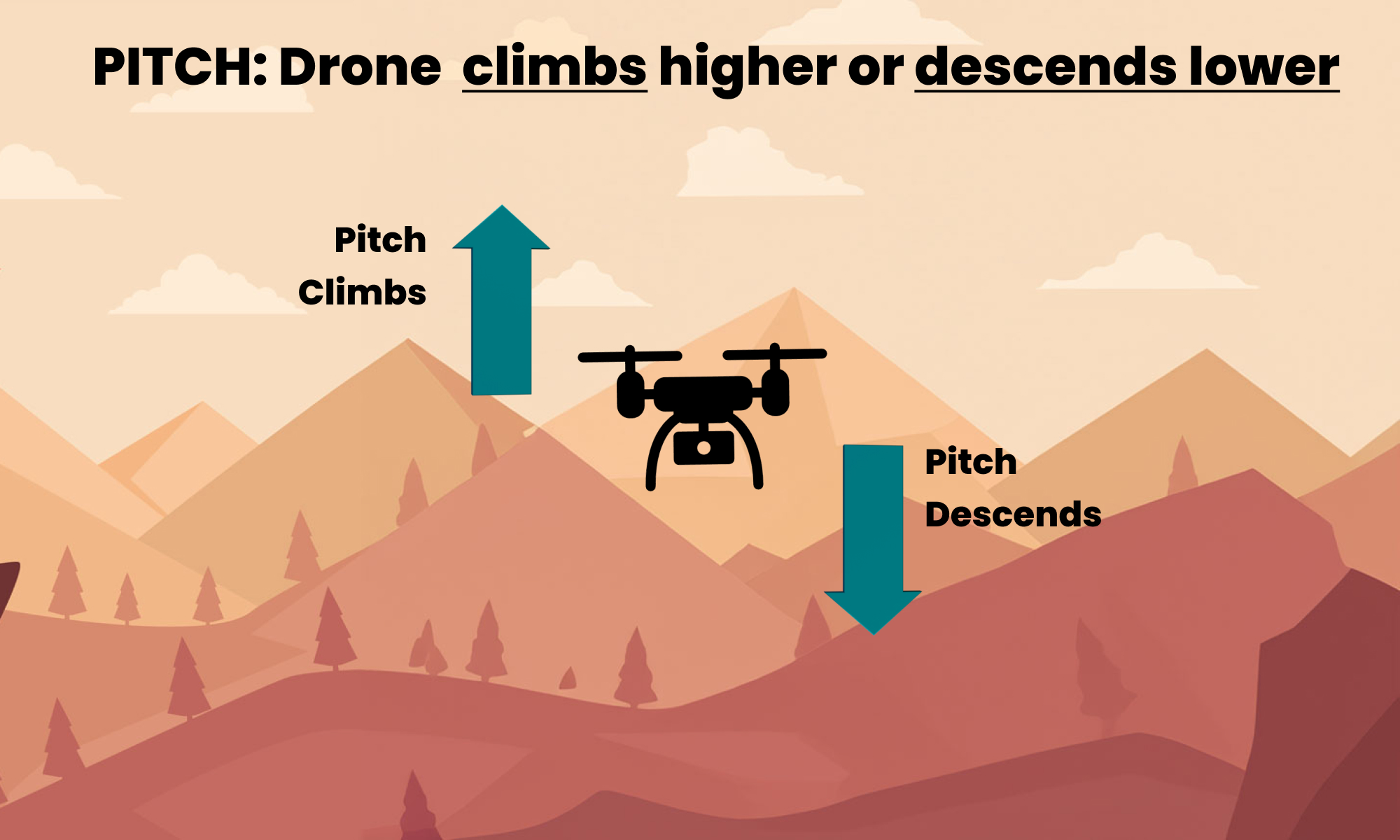
How It Pitch Works
- Component Involved:
- The pitch control is managed by the drone’s stabilizer.
- Function:
- The stabilizer adjusts the tilt of the drone by changing the angle of the propellers. When the stabilizer shifts the motors or propellers up or down, it changes the drone’s pitch.
- Effect:
- If the stabilizer tilts the front down and the back up, the drone pitches forward. Conversely, if the front tilts up and the back down, the drone pitches backward.




